| Categories | Examples |
|---|---|
 |  |
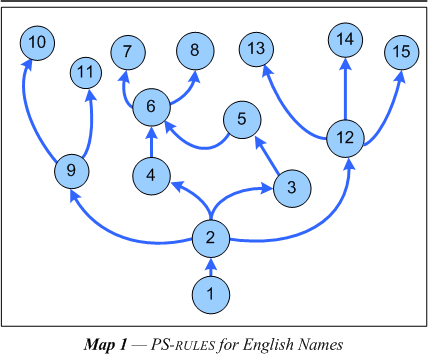
1.8 Categories listed. Each of the various elements categorized by the grammatical rules are explained more fully in the glossary. The reader may click on a particular symbol in the following tables to see the definition, or look it up in the glossary directly. For the most part it is there that the reader will find the analysis that motivated the particular arrangement of the elements in the linguistic structures described. The first listing is of non-terminal elements. These elements appear in rules to refer to structures without single lexical correlates. The list of terminals includes the set of words which should be found associated in the LEXICON with the category symbol in question.
| Categories | Examples |
|---|---|
 |  |
The terminal symbols are those appearing in lexical entries. The turquoise boxes are abstract classes named for their typical functions. These are then realized as words and parts of words, which are listed afterward in light green boxes.
| Categories |
|---|
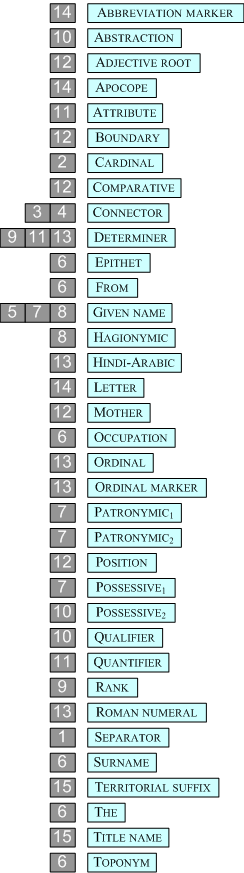 |
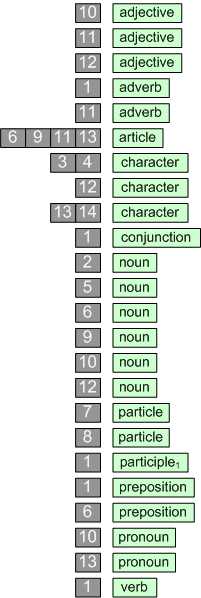
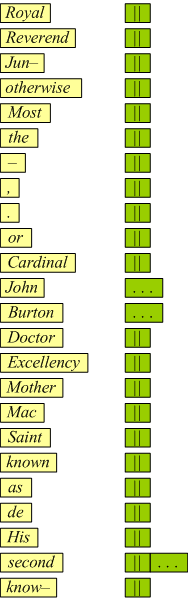
Each item on the list of terminals includes a word or an example of the words which should be found associated in the LEXICON with the both the functional and grammatical categories indicated. The words provided with an ellipsis on the right are from open classes. An open class is one that the language user will discover or invent a word to belong to, i.e., it is added to freely from the vocabulary of the language. A closed class is the opposite, i.e., the set has only certain specifiable words as members. Such classes are indicated with a double Scheffer-stroke to the right; it is possible to be comprehensive and exhaustive with closed classes. The grammatical classes are open or closed only when interpreted in their immediate functional context, otherwise they are all relatively open. In the present formulation, only the two categories: given name, and surname are considered to be open classes — added to at will. The functional classes make most the grammatical categories relatively closed, which means they should allow the investigator to make a comprehensive listing of all possible standard values as members.
| Categories | Example(s) |
|---|---|
 |  |
The following map gives the order and dependence between the various constituent structure rules.